Difference between revisions of "Sehali language"
(→Verbs) |
(→Pronouns) |
||
| Line 629: | Line 629: | ||
|- | |- | ||
!1p | !1p | ||
| − | | | + | |na̤n |
|- | |- | ||
!2s | !2s | ||
Revision as of 18:25, 21 August 2016
Sehali (Sehali: Séẖäli) /sjeħaɫi/ is a language spoken by reptilian people of the same name. Nomadic, the Sehali are known variously as raiders, traders, and slavers, although make their home mostly in the Niuxleb Plains, controlling major tradeways between the Copper Mountains and the Great East Plateau. Their articulators differ to some extent from humans, but not so greatly that their languages are unintelligible or unlearnable to one another.
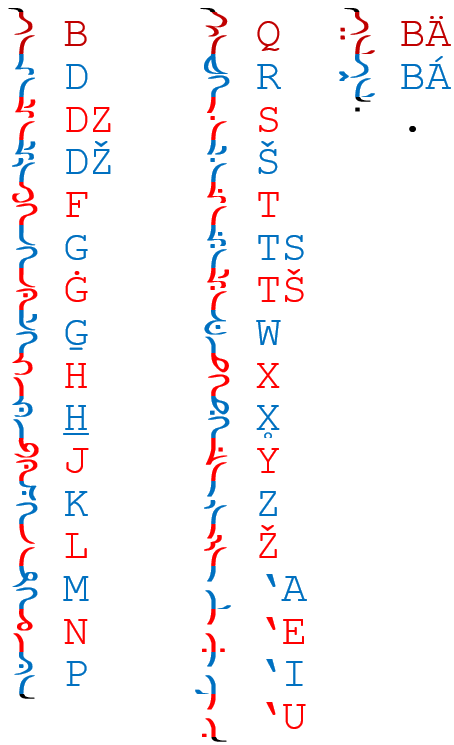
Alphabet
Sehali uses a cursive abjad, written from top to bottom, right to left. Vowel diacritics are optional, while secondary articulation diacritics (to the left of the main character) are mandatory when present.
Phonology
Sehali phonology revolves heavily around the alternation between palatalized, velarized, and pharyngealized consonants. The default articulation is presumed to be velar.
Consonants
| Grapheme | Palatalized | Velarized | Pharyngealized | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | /bj/ | /bγ/ | /bʕ/ | ||||||
| D | /dj/ | /dγ/ | /dʕ/ | ||||||
| DZ | /dzj/ | /dzγ/ | /dzʕ/ | ||||||
| DŽ | /dʑ/ | ||||||||
| F | /ɸj/ | /ɸγ/ | /ɸʕ/ | ||||||
| G | /gj/ | /g/ | |||||||
| Ġ | /ɣj/ | /ɣ/ | |||||||
| G̱ | /ʡ/ | ||||||||
| H | /h/ | ||||||||
| H̱ | /ħ/* | ||||||||
| J | /ʕ/ | ||||||||
| K | /kj/ | /k/ | |||||||
| L | /lj/ | /ɫ/ | /lʕ/ | ||||||
| M | /mj/ | /mγ/ | /mʕ/ | ||||||
| N | /ɲ/ | /n/ | /ŋ/ | ||||||
| P | /pj/ | /pγ/ | /pʕ/ | ||||||
| Q | /qj/ | /q/ | /qʕ/ | ||||||
| R | /rj/ | /rγ/ | /rʕ/ | ||||||
| S | /sj/ | /sγ/ | /sʕ/ | ||||||
| Š | /ɕ/ | ||||||||
| T | /tj/ | /tγ/ | /tʕ/ | ||||||
| TS | /tsj/ | /tsγ/ | /tsʕ/ | ||||||
| TŠ | /tɕ/ | ||||||||
| W | /βj/ | /βγ/ | /βʕ/ | ||||||
| X | /xj/ | /x/ | |||||||
| X̥ | /χj/ | /χ/ | /χʕ/ | ||||||
| Y | /j/ | ||||||||
| Z | /zj/ | /zγ/ | /zʕ/ | ||||||
| Ž | /ʑ/ | ||||||||
| ' | /ʔ/ | ||||||||
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Epiglottal | Glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | Voiceless | Palatalized | pj | tj | kj | qj | ʔ | ||
| Velarized | pγ | tγ | k | q | |||||
| Pharyngealized | pʕ | tʕ | qʕ | ||||||
| Voiced | Palatalized | bj | dj | gj | |||||
| Velarized | bγ | dγ | g | ||||||
| Pharyngealized | bʕ | dʕ | ʡ | ||||||
| Fricative | Voiceless | Palatalized | ɸj | sj | ɕ | xj | χj | h | |
| Velarized | ɸγ | sγ | x | χ | |||||
| Pharyngealized | ɸʕ | sʕ | χʕ | ħ* | |||||
| Voiced | Palatalized | βj | zj | ʑ | ɣj | ||||
| Velarized | βγ | zγ | ɣ | ||||||
| Pharyngealized | βʕ | zʕ | ʕ | ||||||
| Affricate | Voiceless | Palatalized | tsj | tɕ | |||||
| Velarized | tsγ | ||||||||
| Pharyngealized | tsʕ | ||||||||
| Voiced | Palatalized | dzj | dʑ | ||||||
| Velarized | dzγ | ||||||||
| Pharyngealized | dzʕ | ||||||||
| Nasal | Palatalized | mj | ɲ | ||||||
| Velarized | mγ | n | |||||||
| Pharyngealized | mʕ | ŋ | |||||||
| Trill | Palatalized | rj | |||||||
| Velarized | rγ | ||||||||
| Pharyngealized | rʕ | ||||||||
| Approximant | Palatalized | lj | j | ||||||
| Velarized | ɫ | ||||||||
| Pharyngealized | lʕ |
- [ħ] is an allophone of /hʕ/.
Vowels
| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| High | i | u |
| Mid | e | |
| Low | a | |
Sehali marks secondary articulation of consonants upon vowels. When Latinized, a diacritic above the vowel indicates that the consonant preceding that vowel is pronounced with the indicated secondary articulation. A diacritic below the vowel indicates that the consonant following that vowel is pronounced with the indicated secondary articulation.
- Palatalization: tá , ̗at
- Pharyngealization: tä, ̤at
Phonotactics
(C)V(C)
It is important to note that some consonants (DŽ, G̱, H̲, J, Š, TŠ, Y, Ž) can only be in certain environments (palatal, velar, pharyngeal). These remain phonemic (apart from H̲) and still require diacritics.
H̲ represents an allophone of pharyngealized H, but is represented by a separate character in both Latin and Sehali orthography.
The final (third) consonant in a verb root must be velarized.
Grammar
Primarily VSO and head-initial.
- Adjectives follow nouns.
- Determiners and deixis precede nouns.
- Genitive nouns succeed nouns and may include deixis in the phrase.
Number
- Duel suffix: at
- Plural suffix: is
Case
- Genitive case prefix: a̤l
Possession Suffixes
| 1s | na |
|---|---|
| 1p | nü |
| 2s | ti |
| 2p | tü |
| 3s | wa |
| 3d | ma |
| 3p | mi |
Definiteness and Deixis
Preposed particles:
- Indefinite: in
- Proximal: dís
- Mesioproximal: dí̗š
- Mesiodistal: där
- Distal: dar
Verbs
Verbs are defined by roots. They are inflected by tense (past, present, future) and mood (indicative, subjunctive, imperative), and have many derivations.
- Adjectival suffix: zi
- ˈˈˈPassive suffix: w(u)
Indicative Paradigm
| Past | Present | Future | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (base) | wadma (lived) | wadam (live) | wadám (will live) |
| 2 (nominal) | wadmiġ (life) | ||
| 3 (causative) | mawadma (gave birth) | mawdam (give birth) | mawädám (will give birth) |
| 4 (dative) | ziwadma (gave rise to) | ziwdam (give rise to) | ziwadám (will give rise to) |
| 5 (reflexive) | a̤dwadma (remembered) | a̤dwadam (remember) | a̤dwadám (will remember) |
| 6 (reciprocal) | umwadmu (non-existent) | umwadmu (non-existent) | umwadámi (non-existent) |
| 7 (cessative) | axwadmäl (died) | axwadamlï (die) | axwadámlï (will die) |
| 8 (terminative) | uxwadmas (killed) | axwadamsi (kill) | axwadámsi (will kill) |
Subjunctive Paradigm
| Past | Present | Future | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (base) | anufla (burned) | anufal (burn) | anufál (will burn) |
| 3 (causative) | a̤bnufla (made X burn) | a̤bnufal (make X burn) | a̤bnufál (will make X burn) |
| 4 (dative) | aznufla (set fire to) | aznufal (set fire to) | aznufál (will set fire to) |
| 5 (reflexive) | a'nuflaẖ (non-existent) | a'nufalaẖ (non-existent) | a'nufaliẖ (non-existent) |
| 6 (reciprocal) | awanufla̤ẖ (non-existent) | awanufala̤ẖ (non-existent) | awanufáli̤ẖ (non-existent) |
| 7 (cessative) | ax̣anuflal (burnt out) | ax̣anufali (burn out) | ax̣anufáli (will burn out) |
| 8 (terminative) | ux̣anuflas (extinguish) | ux̣anufalsi (extinguish) | ux̣anufálsi (will extinguish) |
Imperative Paradigm
| 1 (base) | šápäna (sail!) |
|---|---|
| 3 (causative) | bišápäna (set sails!) |
| 4 (dative) | ažíšápäna (ship it!) |
| 5 (reflexive) | yá'šápna̤ẖ (return!) |
| 6 (reciprocal) | wa'šápna̤ẖ (fly colours!) |
| 7 (cessative) | g̱äšápänlä (full stop!) |
| 8 (terminative) | g̱äšápänsä (sink it!) |
Adjectives
- Adjectives are inflected as causative verbs in the causative.
Lexicon
Pronouns
| 1s | han |
|---|---|
| 1p | na̤n |
| 2s | tin |
| 2p | nant |
| 3s.an | ẖü |
| 3d.an | ẖüma |
| 3p.an | ẖüm |
| 3s.in | saw |
| 3d.in | sami |
| 3p.in | sam |
Pronoun genitives are formed with a simple suffix: 'i
Pronominal Agglutinations
If both subject and object are pronouns, they are often agglutinated into a single word, omitting a word-final vowel in the subject if present.
Numbers
Base-8.
| 1 | alá |
|---|---|
| 2 | ba |
| 3 | ta |
| 4 | ẖä |
| 5 | xa |
| 6 | ra |
| 7 | za |
| 8 | lám |
| 16 | ešir |
| 24 | tašir |
| 32 | ẖäšir |
| 64 | yémhi |
| 93 | yémhik bašir ta |
Prepositions and Particles
| abaft | istär |
|---|---|
| abeam | ismi̗d |
| aboard | ṳn |
| about | run |
| above | tu̗p |
| across | usidžá |
| afore | isbṳl |
| after | arfit |
| against | g̱ästir |
| along | si̗d |
| amid | sandit |
| aport | ilif |
| around | rud |
| astarboard | iri̤ẖ |
| atop | buwa |
| before | ẖïn |
| behind | fur |
| below | laġ |
| beside | asdi |
| between | yínum |
| beyond | pasit |
| despite | buwin |
| down | dun |
| except | bud |
| following | ifta |
| for | wir |
| from | fun |
| in | i |
| including | wiḡïn |
| inside | inút |
| into | ín |
| like | sum |
| near | nara |
| next | ifa |
| of | u |
| off | fur |
| on | pu |
| onto | til |
| opposite | mirul |
| out | ut |
| outside | udpṳl |
| over | iwar |
| past | biyún |
| since | dan |
| than | mil |
| through | dúral |
| to | a |
| toward | a'i |
| under | unal |
| underneath | unalpṳl |
| unlike | esum |
| until | tis |
| up | ap |
| upon | appu |
| via | wid |
| with | mad |
| without | umad |
| negative (part clit) | e |
|---|---|
| potential | dzï |
Open Class
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1fj-AQQnk_R1mG7-qFpU_AXwnH9QqRVsau1wvRvjVWgQ/edit?usp=sharing